The App Store ecosystem today is home to nearly 2 million apps. That means finding new apps to download is now more challenging than ever. This, in turn, leads app developers to funnel more money into App Store Search ads, traditional SEO and digital advertising in an effort to acquire new users. A new feature called App Clips, arriving in iOS 14 later this year, will give developers another option to introduce their app to users. With App Clips, users can instead load just a small part of an app on demand, when required. And when they’re done, the App Clip disappears.
The concept behind App Clips isn’t new. Google’s Android platform has for several years offered tiny app-on-demand downloads called “Instant Apps.”
Like Instant Apps, Apple’s App Clips are about making apps as seamless to use as the web. They are fast, ephemeral and eliminate the barrier to entry that is downloading an app from the App Store.
Today, many users don’t want to bother with a full app download when they’re in a hurry. For example, if a user is trying to pay for parking, they’re more likely to swipe their credit card in the meter to save time, instead of downloading the city’s parking app.
A customer waiting in line to place a food or drink order also doesn’t want to bother downloading the restaurant’s app to browse a menu and pay — they’ll just speak their order at the counter. And a customer wanting to rent a scooter just wants to tap, pay and be on their way.
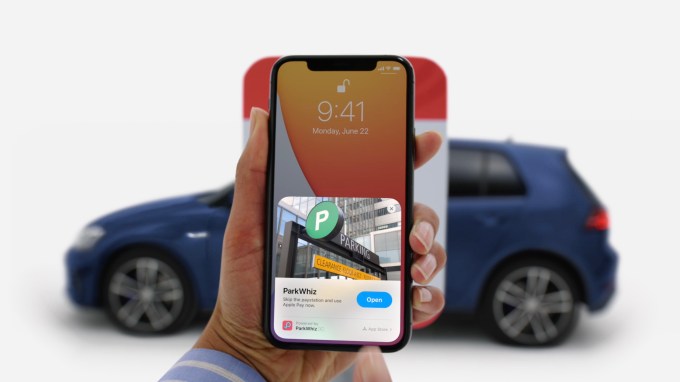
Image Credits: Apple
An App Clip would work in any of of these scenarios, and many others, by making it as easy to use apps as it is to tap to check out with Apple Pay or launch a website.
While Apple will allow users to launch clips by way of a QR code, a new “App Clip Code” arriving later this year will offer an upgraded experience to kicking off these apps you find suggested to you out in the real world. App Clip Codes will combine both NFC and a visual code, so users can either tap or scan the code to access the App Clip experience.

Image Credits: Apple
For example, an App Clip Code placed on a parking meter would allow a user to quickly load just the part of the app where they pay for their time. They can even skip manual credit card entry by using Apple Pay, if included in a given App Clip.
The App Clips themselves are less than 10 MB in size and ship bundled with the app on the App Store. They’re built using the same UI technologies developers use today to build apps, like UIKit or SwiftUI. But using an App Clip doesn’t trigger the app to download to the user’s device.
A key advantage App Clips offer is how they address concerns over data privacy. Because App Clips are essentially a way to run app code on demand, they’re restricted from tapping into iPhone’s more sensitive data — like health and fitness information, for example. Plus, the App Clip and all its data will automatically disappear if it’s not used again within some period of time.
However, if a user begins to launch a particular App Clip more regularly — perhaps one for their favorite coffee order at their local shop, for instance — the App Clip’s lifetime is extended and it can get smarter. In this example, the App Clip could cache the customer’s last order and present it as a recommendation, to speed up the ordering process. Eventually, this repeat user may decide to download the full app.
In that case, the hand-off is seamless as well — iOS will automatically migrate the authorizations for things like Camera, Microphone and Bluetooth access, which the App Clip had already requested. Select data can also be migrated.
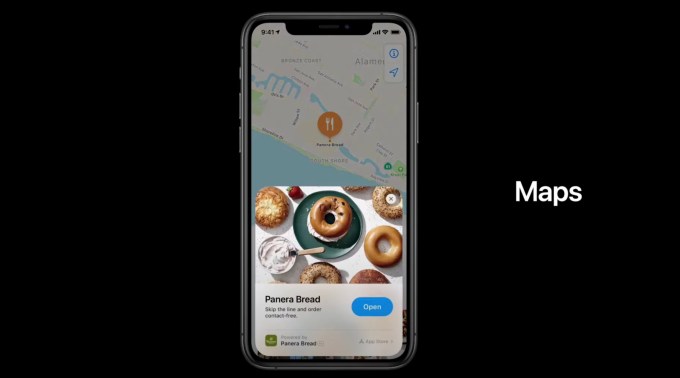
Image Credits: Apple
There are other ways for users to encounter App Clips besides out in the real world, though that may be a primary use case.
Apple says App Clips can be sent as links in iMessage, popped up as a suggestion when you’re browsing a mobile site in Safari, shown on a business’s details page in Apple Maps or may appear in Siri’s Nearby suggestions.
The idea is that wherever a user may be on their device — or out in the world — the App Clip can be there, too.


Recent Comments